Interstellar overhype: Nasa debunks claim about alien-made comet | Comets
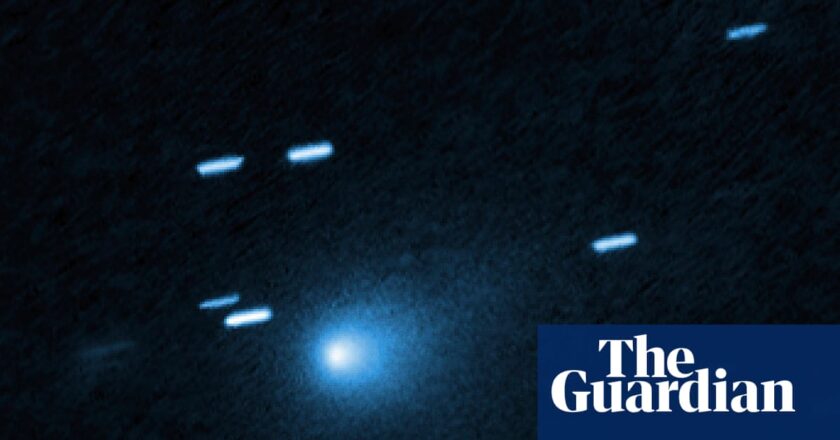
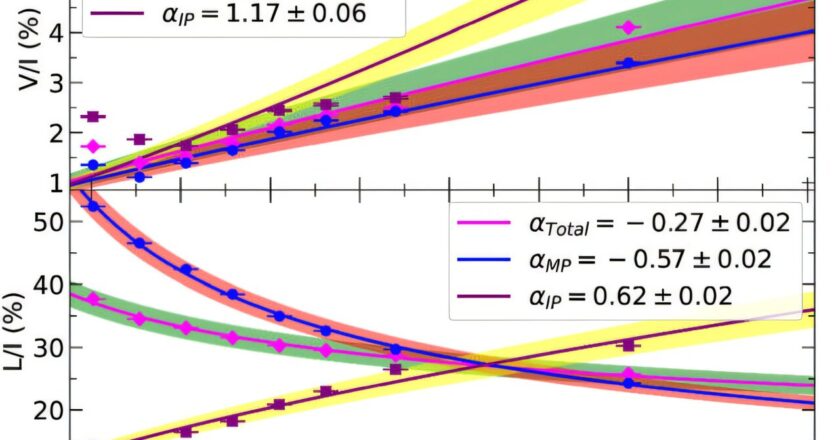
Skywatchers at Nasa have discounted a Harvard astronomer’s hypothesis that a rare interstellar object hurtling through our solar system is a relic from a civilization in another celestial neighborhood, and “could potentially be dire for humanity”.Avi Loeb, head of Harvard University’s Galileo Project, which searches for evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence, raised eyebrows by suggesting in a scientific paper in July that Comet 3I/Atlas, set for a close pass with Mars next month, could be artificially made.It is only the third known object originating outside the solar system to pass through and was named for the Asteroid Terrestrial-Impact Last Alert System (Atlas) survey telescope in Río Hurtado, Chile, that discovered it on 1 July.Loeb says observations of the object so far have not...