Don’t miss Saturn at opposition – Astronomy Now
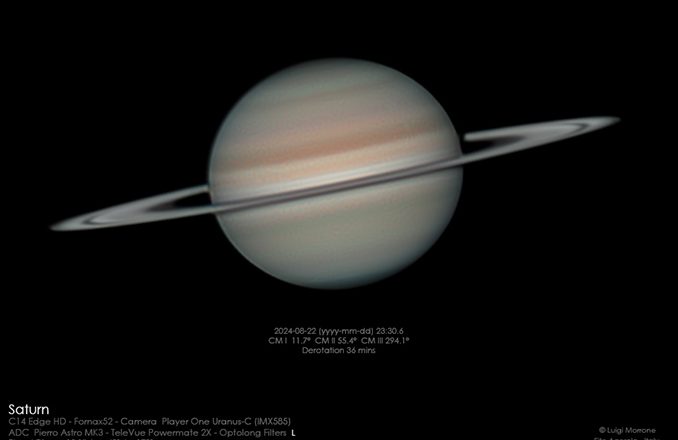
Saturn imaged on 22 August 2024, showing the narrow tilt of its splendid rings. Image: Luigi Morrone.
Saturn is arguably the most popular planet, certainly with children and the public at large. Its wonderful system of rings, well seen through even a small telescope, makes it unique in the Solar System.
Unlike Mars and Jupiter, both of which are currently rising high in the Taurus/Gemini area, Saturn lies rather low in the sky from UK shores, among the stars of the largely Southern constellation of Aquarius. Despite this, Saturn still achieves a reasonable altitude of between 26° and 31° from UK shores when it culminates at about 1am in early September. Town and city dwellers just need to find a reasonably flat horizon from the south-west around to the south-east to view Saturn clear loc...